The 2020 Okavango Delta flood is described as being one of the biggest in the last years.
Here are some key explanations and figures to help you understand this unique phenomena and the exceptional ecosystem associated…!
The Okavango delta was created around 40 000 years ago due to a tectonic movement.
The Okavango River originates in the Angolan highlands as two rivers, the Cuito and Cubango join to form the 1 500 km long Okavango River.
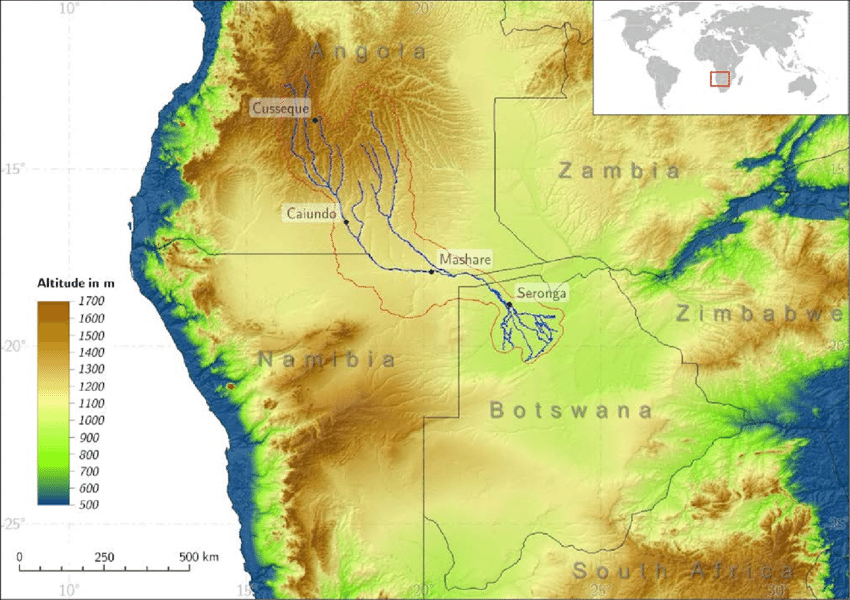
Topographic map showing a global view of the Okavango delta in Botswana and its origins on the Angola plateau (© Weinzierl 2015).
It takes 4 months to the water to arrive from Angola plateau.
Once it enters Botswana, water takes 1 to 2 months to meander through the main 190 kilometre long channel of the Panhandle from Mohembo to Seronga. Then from the head of
the alluvial fan at Seronga, the water takes another 2 to 3 months before reaching the lowest, most distal reaches of the Delta along the Thamalakane, lower Kunyere and Khwai Rivers.
The annual inflow range is between 7 000 and 15 000 million cubic meters, of which 97% is lost by evaporation.
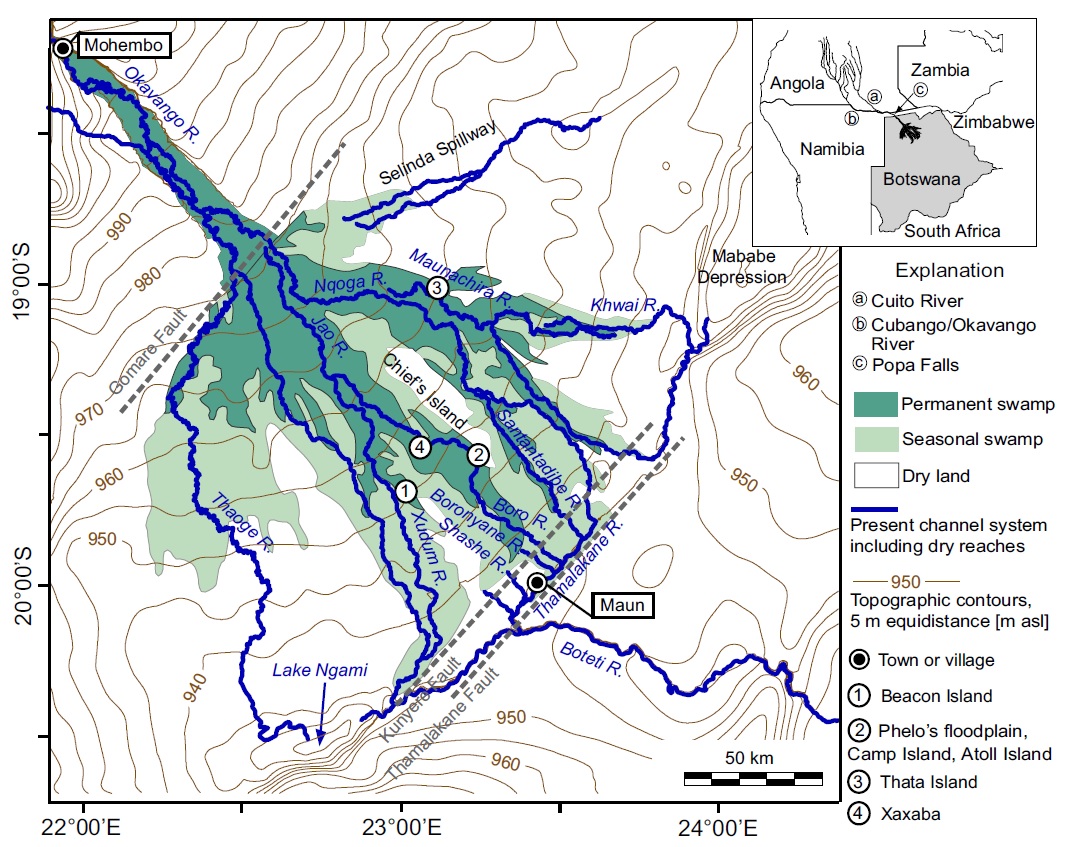
Okavango-Delta-rivers-and-ecosystems_- Copyright-Milzow-and-al-2009
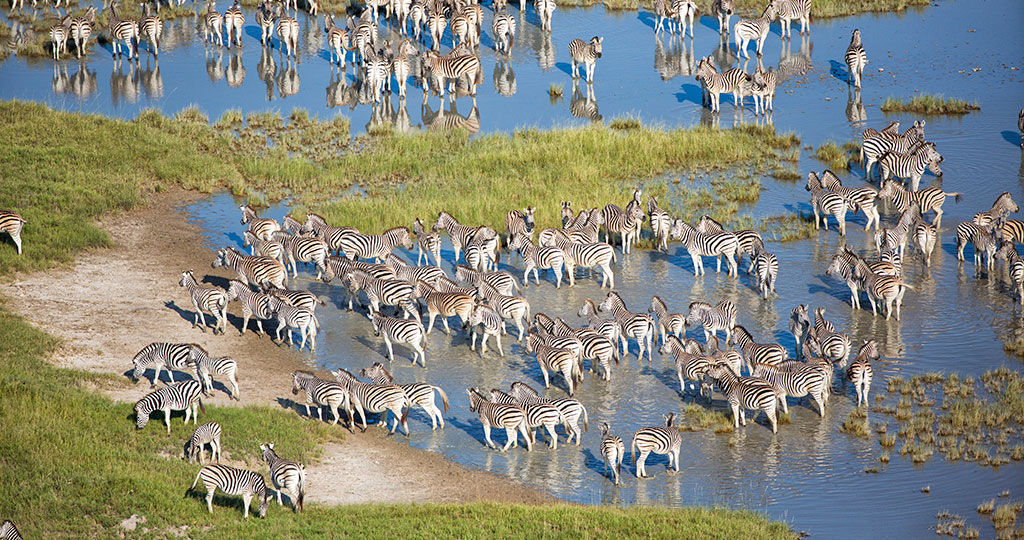
The delta area comprises approximately 6 000km² of permanent swamps, with seasonal swamp variation of 4 000km² up to 20 000 km².
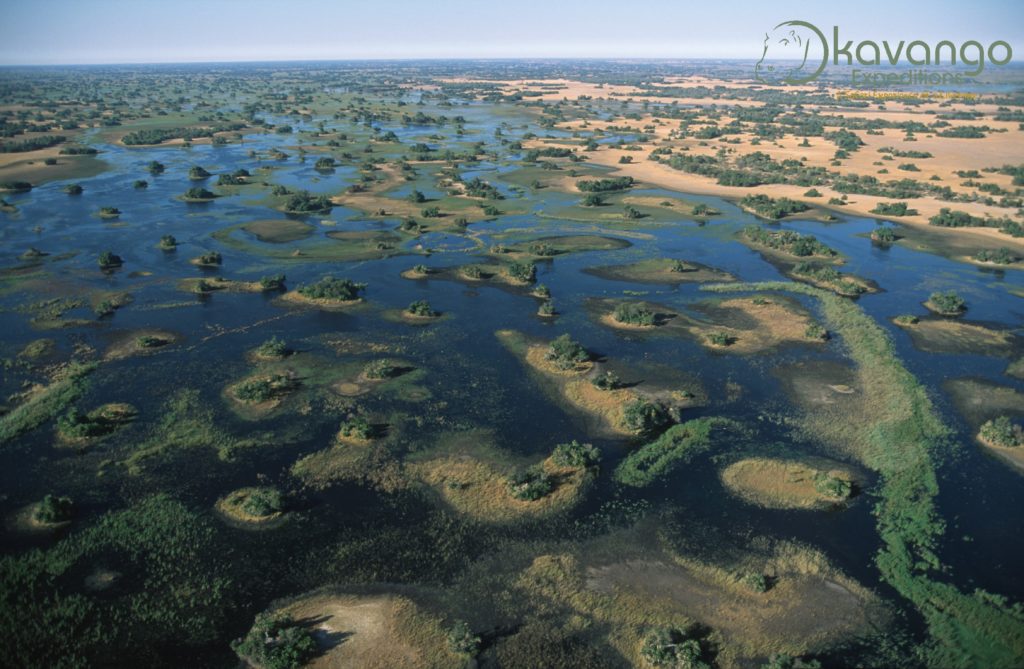

Aerial view of islands and waterways of Central Okovango © M. Harvey
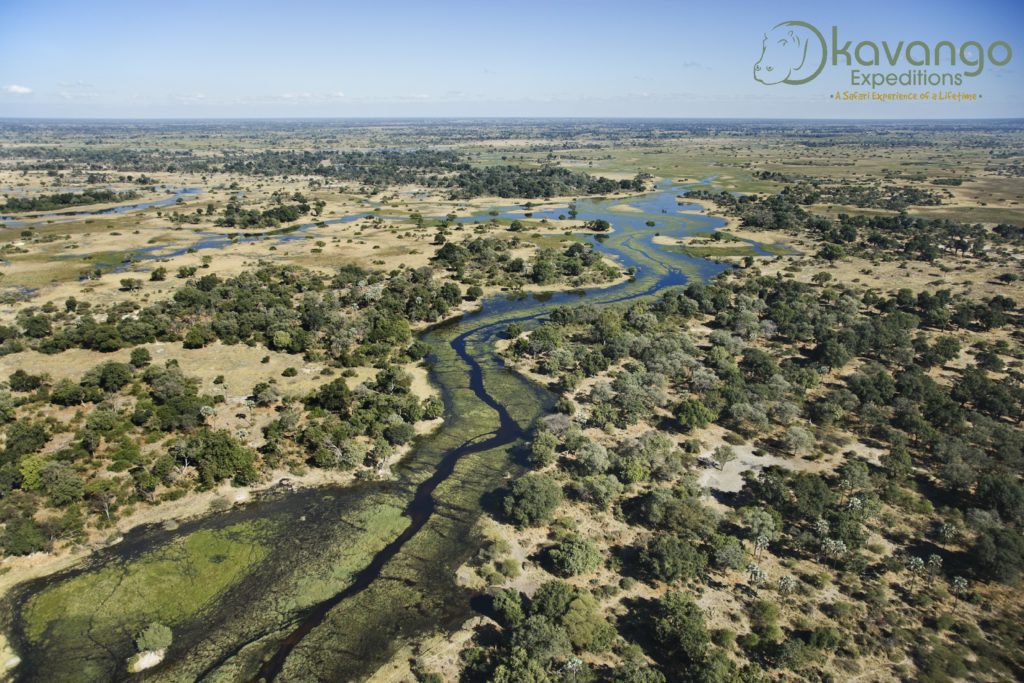

Aerial view of islands and waterways of the Okavango Delta. Botswana © M. Harvey.
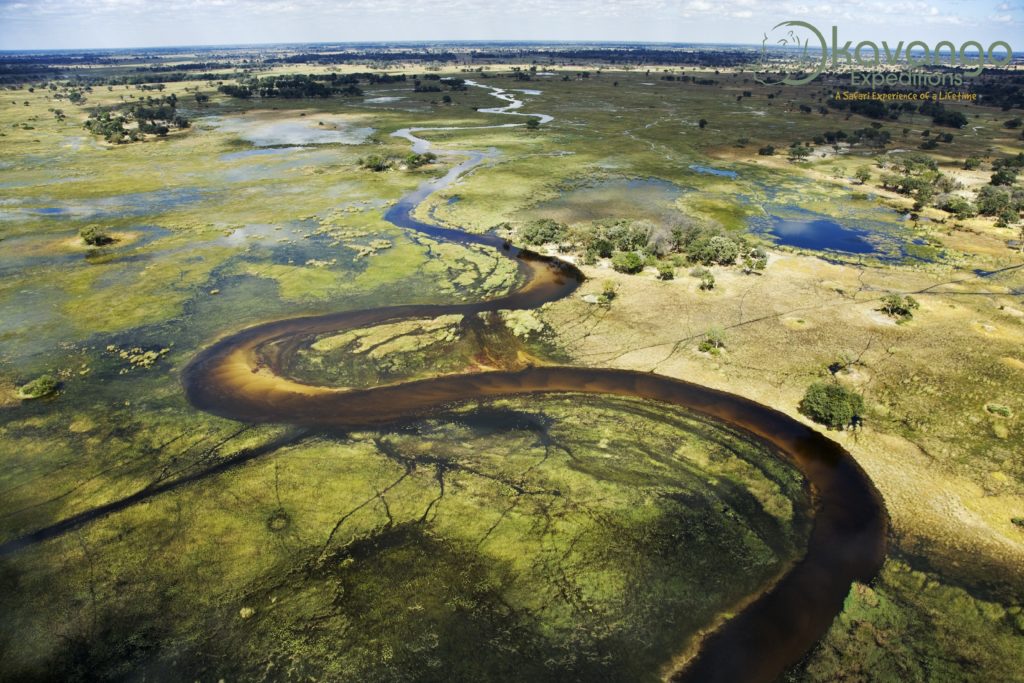

Waterways of the Okavango Delta. Botswana. © M. Harvey
The flood is transporting an average of 170 000 tons of sediments each year.
The Okavango Delta has a rich plant species assemblage, with a total of 1068 species of flowering plants and ten species of ferns.
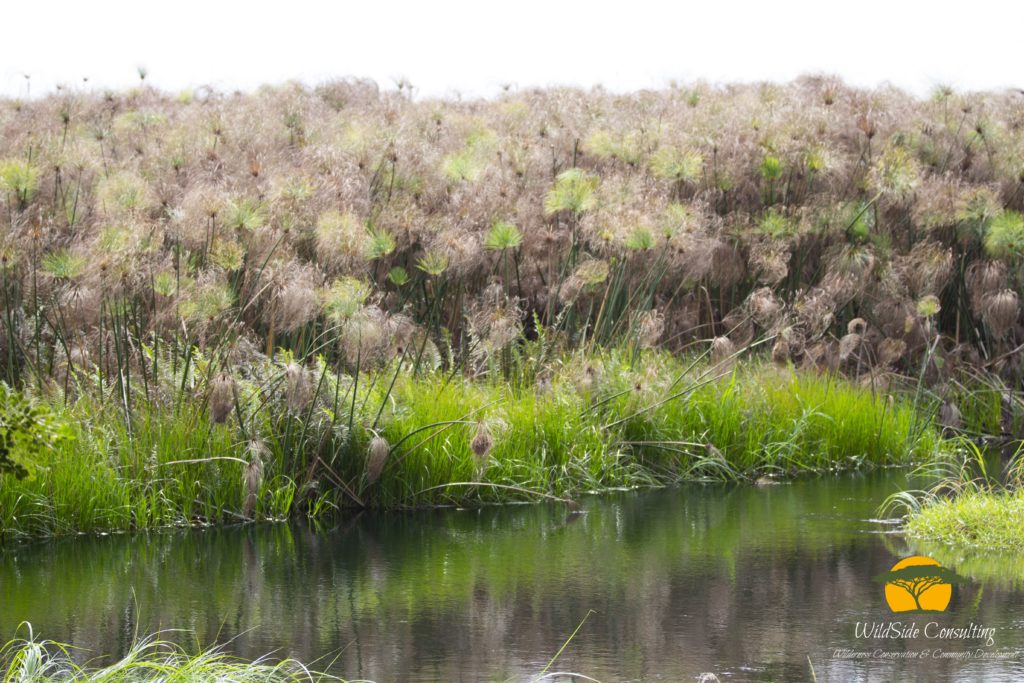

Papyrus and reeds fields of the Okavango delta – Botswana. © A.Fleury
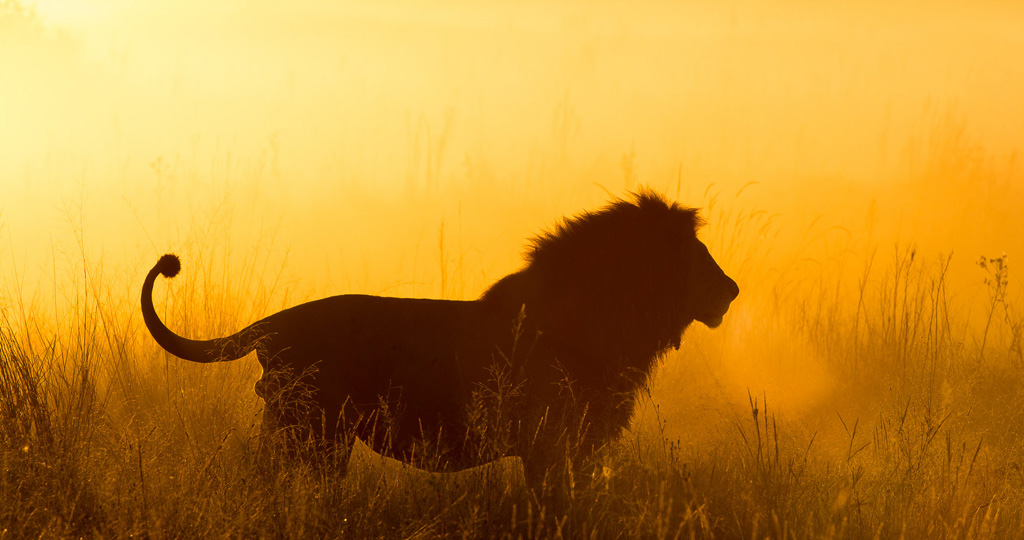
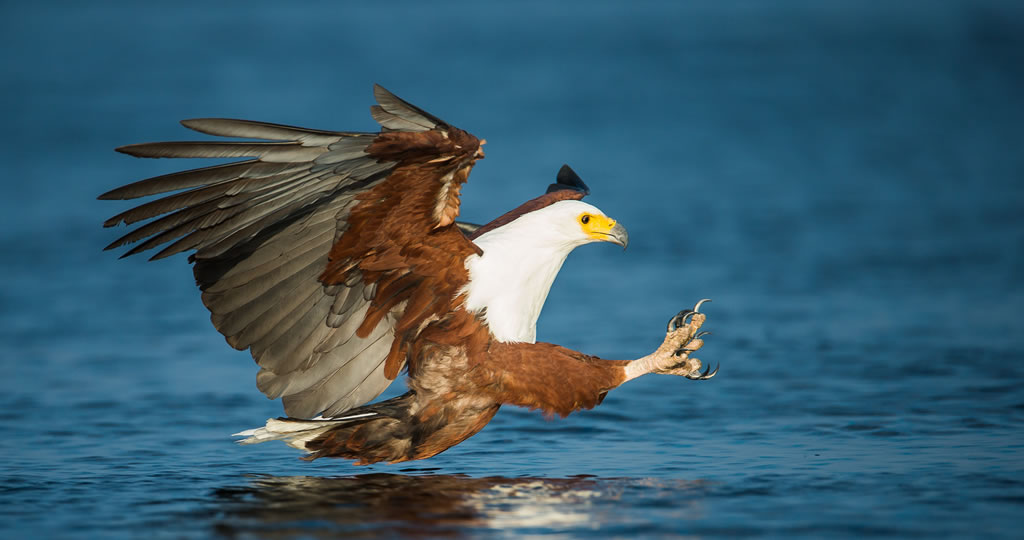
The Okavango Delta ecosystem is also a refuge for an outstanding fauna: Aquatic fauna represents 208 species, including 90 species of fish. There are over mammal 130 species, over 480 bird species, 64 reptiles, 33 amphibians, 94 dragonflies, and 115 butterfly species!
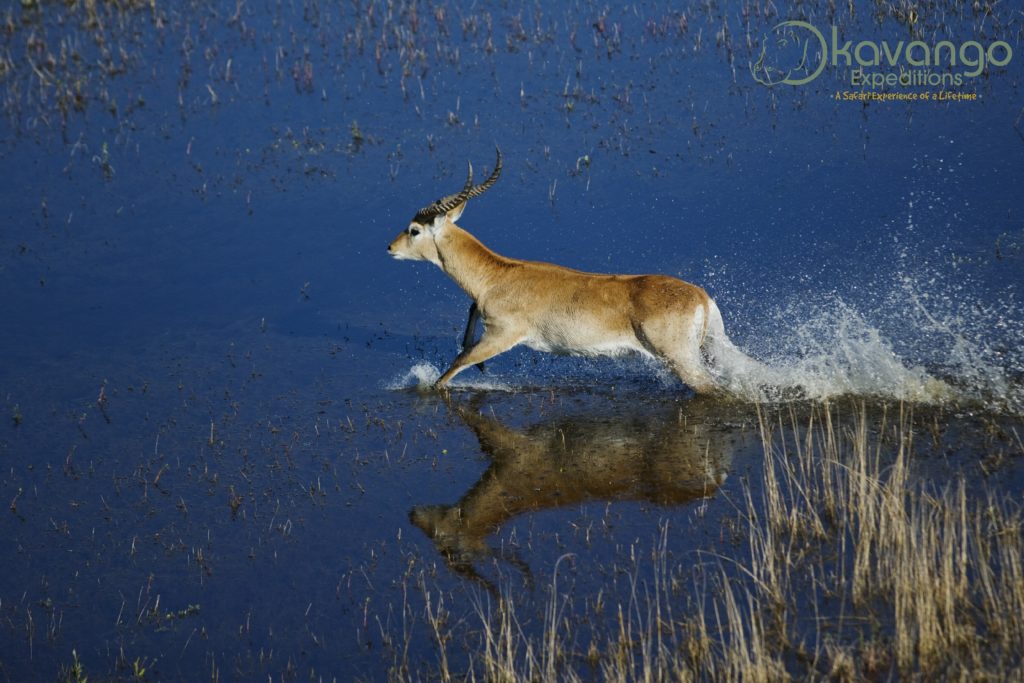

Red Lechwe (Kobus leche) which is the most common antelope found in the Okavango Delta. The hind legs are somewhat longer in proportion than in other antelopes, to ease long-distance running in marshy soil. © M. Harvey
The Okavango Delta is an extraordinary example of the synergy between climatic, geomorphological, hydrological, and biological processes that show how plants and animals have adapted their lifecycles to the annual cycle of rains and flooding.
Discover our mobile safaris in the Okavango Delta : www.okavangoexpeditions.com







